COMPUTER HARDWARE
A computer is a combination of two terms Hardware and Software. The physical components of a computer are called hardware. Pieces of hardware may be categorized according to the functions each performs: input, process, output, and storage. Your PC (Personal Computer) is a system, consisting of many components. Some of those components, like Windows XP, and all your other programs, are software. Software is the source of interaction between the user and the computer. It represents programs, collection of several sets of instructions, which allow the hardware to run properly. The stuff you can actually see and touch, and would likely break if you threw it out a fifth-story window, is hardware.
Computer Hardware Hardware of a computer is made up of complex electronic circuits. For a user the details of the circuitry are not important. However, the hardware units with which a user has to interact must be clearly understood. For convenience, the hardware of a computer can be classified in the following categories:
1. Input Devices
2. Output Devices
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU)
4. Memory or Storage
5. Motherboard
Let us discuss each of these hardware components:
1. Input Devices: The form in which data is available to a user is not always in the same formas is accepted by computer hardware. Input devices are hardware equipment that receive data and instructions from users, convert the data and instructions into a form that can be processed by the computer and passes the same to the computer. Hence, if you have to enter employees’ names into the computer you do not have to write it on a piece of paper and shove the paper inside the computer. You will need some input device for this. Example: A keyboard is an example of input device.
2. Output Devices: The result, produced by a computer after processing, is not always in user readable form. An output device is hardware equipment that translates this non-readable result into a form understood by the users. Example: A VDU (Visual Display Unit) or monitor is an example of output device.
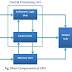
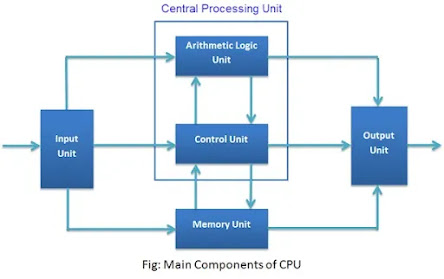
3. Central Processing Unit (CPU): Central processing unit is to computer what brain is to our body. It is the master organ of a computer. No computer can exist without a CPU. It is composed of two simpler hardware units - Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU). CU controls all the activities of other hardware units while ALU performs all the calculations. Computer CPUs are very fast in their calculations and swift in control.
4. Memory or Storage: This hardware is the place where a computer stores all the data and instructions given to it. The results of the processing are also stored here. A computer has many types of memories. Some memories are directly connected to the CPU and are extremely fast as far as storage and retrieval of data is concerned. These memories are called primary memory - RAM (Random Access Memories) and ROM (Read Only Memories) belong to this category of memories. The CPU takes data and instructions stored only in the primary memories.
Primary memories are also of various types. The one that looses its contents when power is switched off is known as volatile memory such as RAM. Some memories retain the data and instructions stored on them even after the power is switched off such as ROM. These memories are known as non-volatile memories.
Secondary storage devices are placed outside the system unit and can be carried from one system to another allowing portability of data and instructions. Floppy disks or diskettes, hard disks and CD-ROM are some of the secondary storage devices. Input devices, output devices and secondary storage devices are not directly connected to the CPU and hence are known as peripheral devices or simply peripherals.
5. Motherboard: Motherboard, also called as System Board, is the most important hardware Notes component of a microcomputer. Motherboard is so called as all the other boards (printed circuit boards having chips or other electronic components) of the computer are connected to this board, hence it is like the mother of all other boards.
Now we will discuss the components of computer hardware in detail.
Central Processing Unit Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the main component or “brain” of a computer, which performs all the processing of input data. Its function is to fetch, examine and then execute the instructions stored in the main memory of a computer. In microcomputers, the CPU is built on a single chip or Integerated Circuit (IC) and is called as a Microprocessor. The part of a computer (a microprocessor chip) that does most of the data processing, the CPU and the memory form the central part of a computer to which the peripherals are attached. The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the part of a computer that interprets and carries out the instructions contained in the software.
The CPU consists of the following distinct parts:
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): The arithmetic and logic unit of CPU is responsible for all arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication and division as well as logical operations such as less than, equal to and greater than. Actually, all calculations and comparisons are performed in the arithmetic logic unit.
Control Unit (CU): The control unit is responsible for controlling the transfer of data and instructions among other units of a computer. It is considered as the “Central Nervous System” of computer, as it manages and coordinates all the units of the computer. It obtains the instructions from the memory, interprets them and directs the operation of the computer. It also performs the physical data transfer between memory and the peripheral device.
Registers: Registers are small high speed circuits (memory locations) which are used to store data, instructions and memory addresses (memory location numbers), when ALU performs arithmetic and logical operations. Registers can store one word of data (1 word = 2 bytes & 1 byte = 8 bits.) until it is overwritten by another word. Depending on the processor’s capability, the number and type of registers vary from one CPU to another. Registers can be divided into six categories viz. General Purpose Registers, Pointer Registers, Segment Registers, Index Registers, Flags Register and Instruction Pointer Register, depending upon their functions. The detailed functions of each and every register is beyond the scope of this book.
Buses: Data is stored as a unit of eight bits (BIT stands for Binary Digit i.e. 0 or 1) in a register. Each bit is transferred from one register to another by means of a separate wire. This group of eight wires, which is used as a common way to transfer data between registers is known as a bus. In general terms, bus is a connection between two components to transmit signal between them. Bus can be of three major types viz. Data Bus, Control Bus and Address Bus. The data bus is used to move data, address bus to move address or memory location and control bus to send control signals between various components of a computer.
Clock: Clock is another important component of CPU, which measures and allocates a fixed time slot for processing each and every micro-operation (smallest functional operation). In simple terms, CPU is allocated one or more clock cycles to complete a micro-operation. CPU executes the instructions in synchronization with the clock pulse.The clock speed of CPU is measured in terms of Mega Hertz (MHz) or Millions of Cycles per second. The clock speed of CPU varies from one model to another in the range 4.77 MHz (in 8088 processor) to 266 MHz (in Pentium II). CPU speed is also specified in terms of Millions of Instructions Per Second (MIPS) or Million of Floating Point Operations Per Second (MFLOPS).












 – a physical device that is used to store data, information and program in a computer.
– a physical device that is used to store data, information and program in a computer.


 Programming language – assembly language
Programming language – assembly language Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)
Main electronic component – integrated circuits (ICs)

 Main electronic component – very large-scale integration (VLSI) and microprocessor.
Main electronic component – very large-scale integration (VLSI) and microprocessor.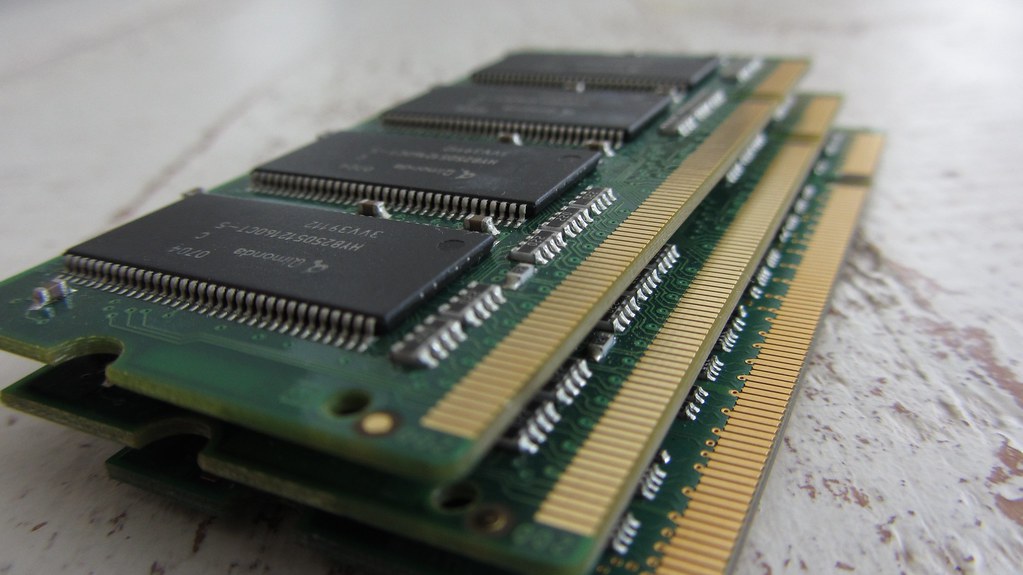 ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off).
ROM (read-only memory) – a type of data storage used in computers that permanently stores data and programs (non-volatile: its contents are retained even when the computer is turned off). Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
Input / output devices – keyboard, pointing devices, optical scanning, monitor, printer, etc.
 Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence, uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method.
Main electronic component: based on artificial intelligence, uses the Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI) technology and parallel processing method. Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognise voice / speech), light scanner, printer, etc.
Input / output device – keyboard, monitor, mouse, trackpad (or touchpad), touchscreen, pen, speech input (recognise voice / speech), light scanner, printer, etc.